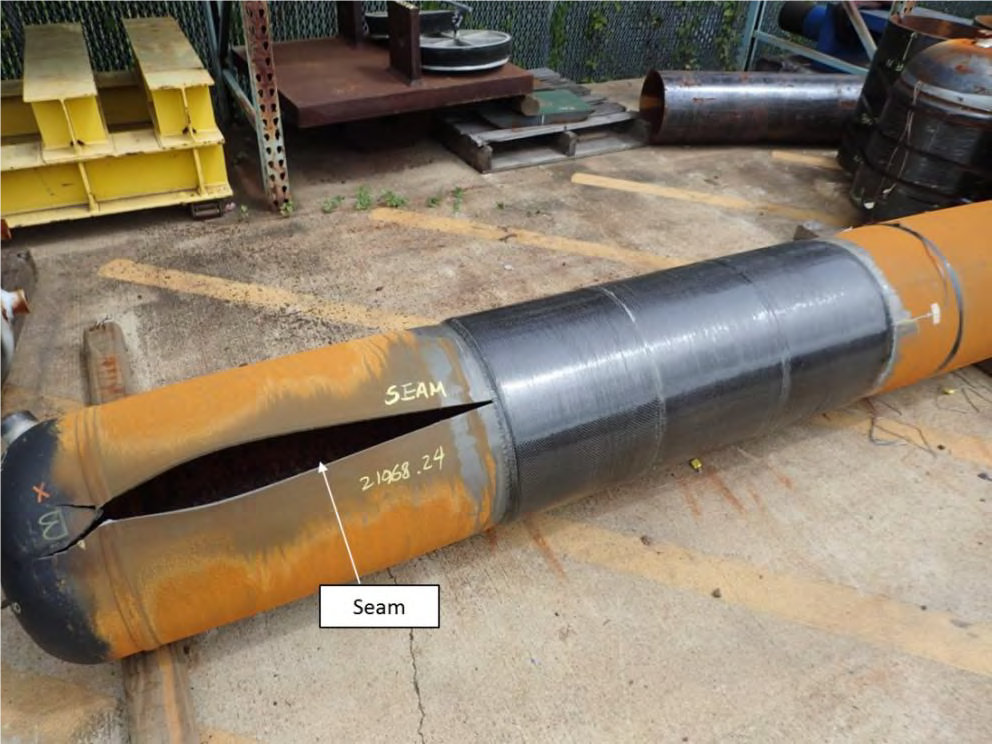
With the development of more accurate in-line inspection tools, the pipeline industry has started to discover a large number of potential defects associated with the pipe’s seam weld. Many of these cases are associated with manufacturing defects and are unlikely to pose a threat to operations. However, when they are identified, the conservative approach has been to replace the defected section of pipe or weld a steel sleeve over it as a permanent repair. In many cases, these options provide a large cost burden for a defect with no history of growth or near-term threat. With increasing testing and design capabilities, composite repairs can successfully help remediate the issue and provide owners/operators an additional, reliable tool in pipeline crack repair.
TEST HISTORY
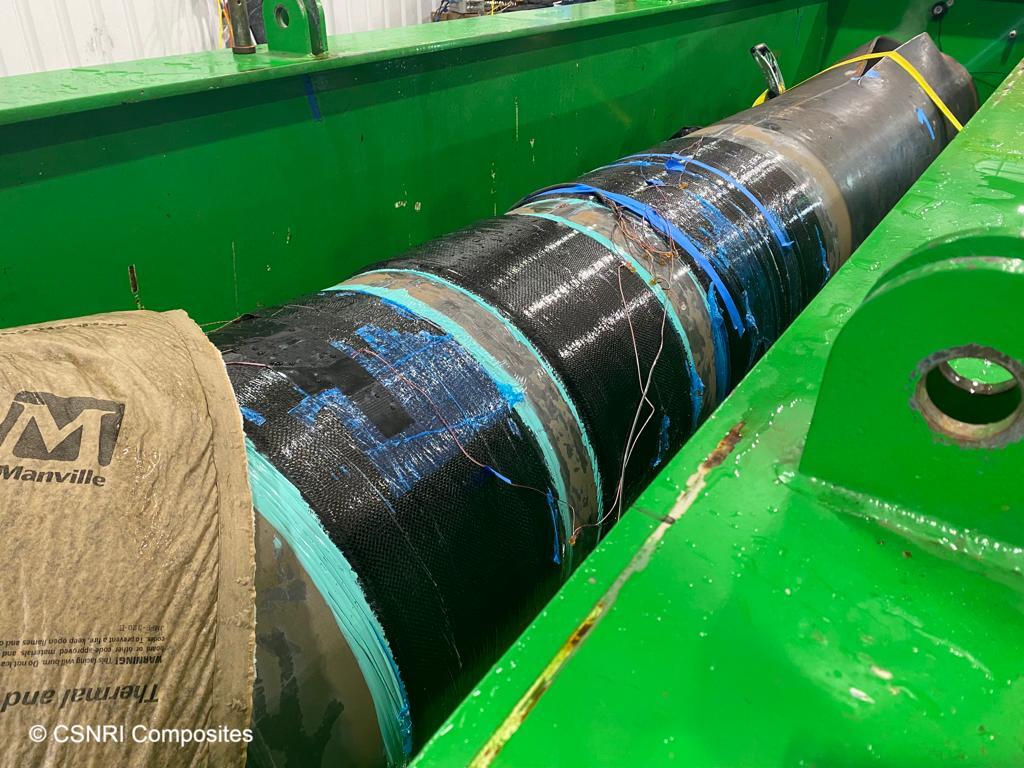
In 2015, the AtlasTM product was thoroughly tested on seam weld cracks 33% and 75% deep. This program, with PHMSA’s involvement, led to the repair of a few dozen permanent repairs on an Ethylene line with low crack depths – close to the 33% depth tested. This line could not be easily welded on or de-pressurized without incurring a major expense but with the use of composites, conservative repairs could be on the live line with minimal expense. Further testing was performed on the Atlas system in a joint industry project examining cracks of 15% and 50% depth. Again, the results here showed tremendous success in not only burst pressure restoration but also demonstrated the composites ability to greatly reduce a crack’s propagation rate – essentially increase the cyclic life of the pipe. Beyond just demonstrating pass/fail scenarios, CSNRI has gone further and developed a predictive tool utilizing classical fracture mechanics and composite theory to determine the remaining capability of a repaired crack defect.
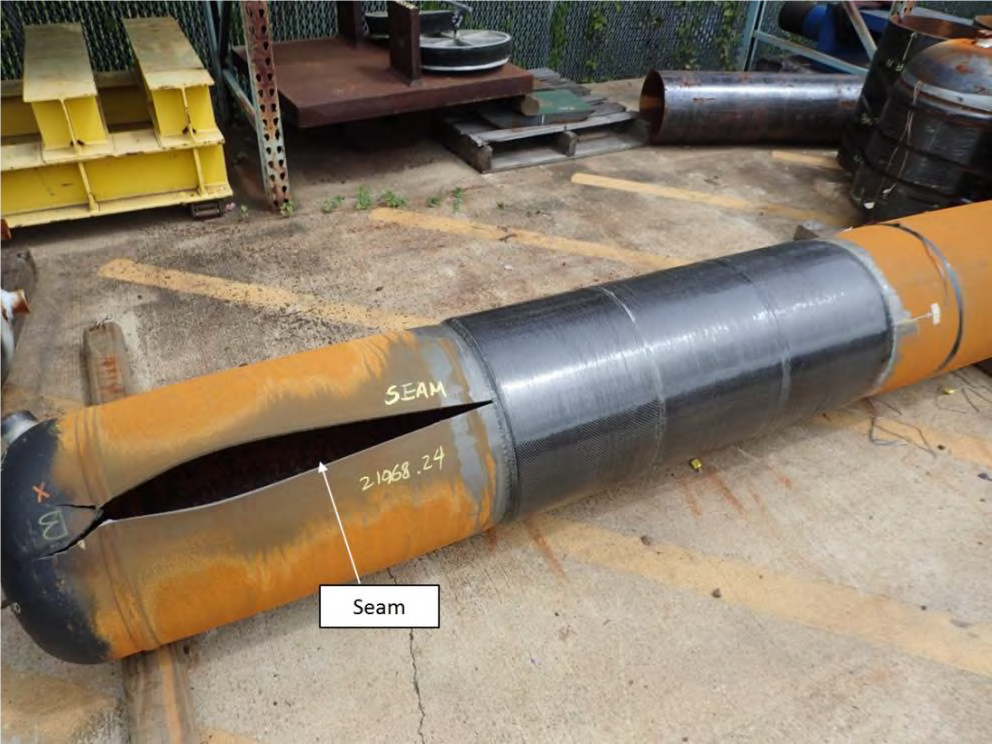

A third major test program provided an ideal scenario to test the prediction of this program to actual results. Before testing the pipe samples, material properties such as fracture toughness were determined. After testing and comparing near 60 samples in both burst and cyclic failures this tool has been shown to be very conservative in its assumptions. Now composite repairs can be installed on crack-like seam weld defects with more confidence than ever knowing that a tested fracture mechanics model supports the engineering design.
LIMITATIONS
Having already proven that they can work on crack and crack-like features there are still many situations where a composite should only be considered as a temporary repair. Current recommendations are that any severe cracks experiencing heavy cycling should only be treated as temporary. A temporary composite repair in this case generally means that a longer-term solution, such as pipe replacement, will be done at a more convenient time. These temporary repairs can be designed to prevent near-term burst and will slow the propagation rate of any pipeline cracks underseeing cyclic conditions. Additionally, in the event that a crack does fail under the repair, the mode of failure changes to a lower-risk leak.
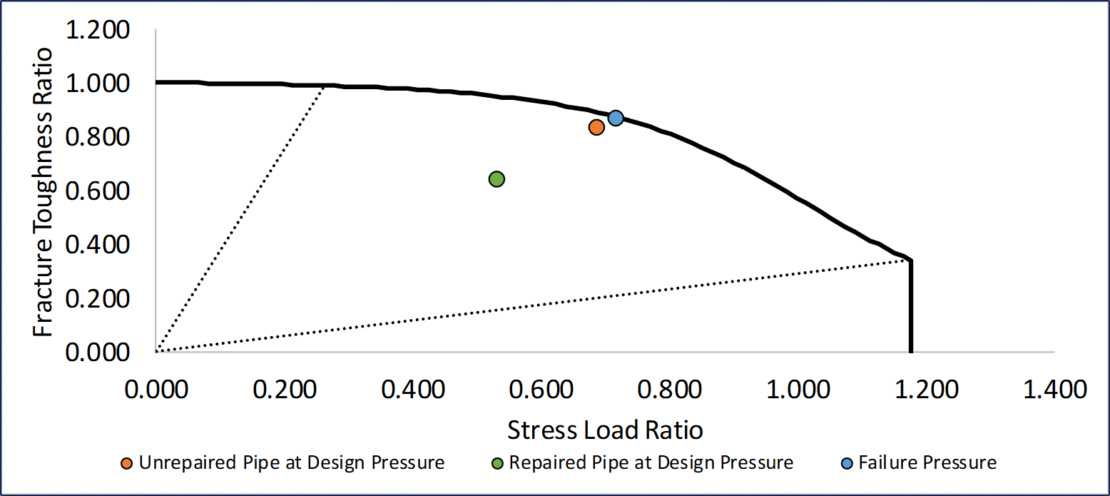
On the other hand, permanent repairs can be installed and supported with documentation in cases with generally low penetration and reasonable cycling conditions. The crack or crack-like feature can then be monitored with standard maintenance and inspection programs to show that an acceptable growth rate, or none, is resent. For more information on how composite repairs, backed with strong engineering, can help with your crack or crack-like defects, please contact sales@cs-nri.com.

Pipeline Crack Repair with Composites
In this TEC talk Casey Whalen, CSNRI's Global Engineering Manager, discusses how a composite repair can help reinforce cracks and extend the service life of pipelines and pipework. This TEC talk will discuss cracks on seam welds, but will also lightly touch on non-seam weld cracks, such as SCC or on girth welds.

Composite Repair Technologies: Pipeline Crack Repair
Listen to CSNRI presentation on Composite Repair Technologies during the 2021 IDT Expo's Workshop on Pipeline Crack Assessment and Repair workshop.
Examining the repair capability of composites on crack or crack-like features
Listen to CSNRI presentation on crack repair during the 2021 Pipeline Technology Conference (PTC).
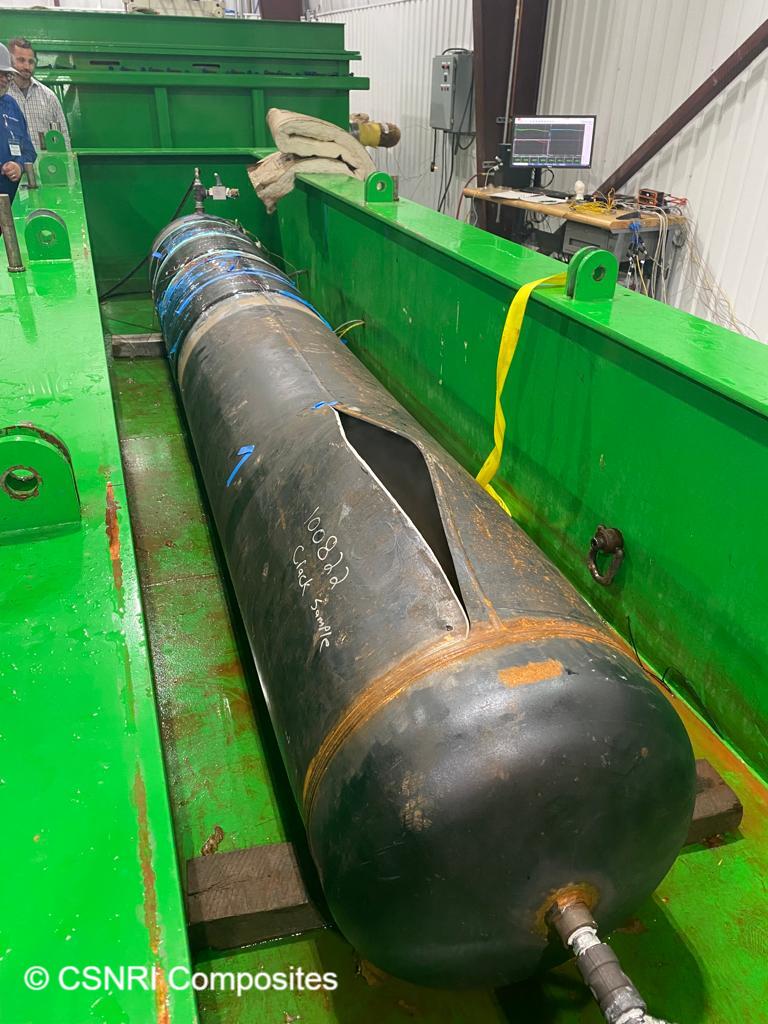
Burst Test on Seam Weld Anomaly
This testing further validated CSNRI's fracture mechanics model and successful high temperature design on 50% deep seam weld anomalies. This technology is enabling operators to reduce cut outs and greenhouse gas emissions while mitigating complex pipeline integrity threats.
Owners of an energy exploration, production, and storage company in Colombia, observed damage caused by external corrosion to 30-inch diameter process lines at air/ground interfaces. Promptly responding to the issue, the process line owners requested a repair design that would structurally rehabilitate the corrosion damage to the lines. Local CSNRI partner installed a four-layer application of Atlas to restore the lines to their original design capacity, extending service life.












