As the use of horizontal directional drilling (HDD) and similar trenchless technologies has increased, so has the need to protect the pipeline coating during installation. With this increase in usage scope comes increased usage in less-than-favorable geographies. Where it was traditionally used in silt, sand, or clay soils, it is now being increasingly performed in rocky soils, creating more harsh conditions for the pipeline and coating.
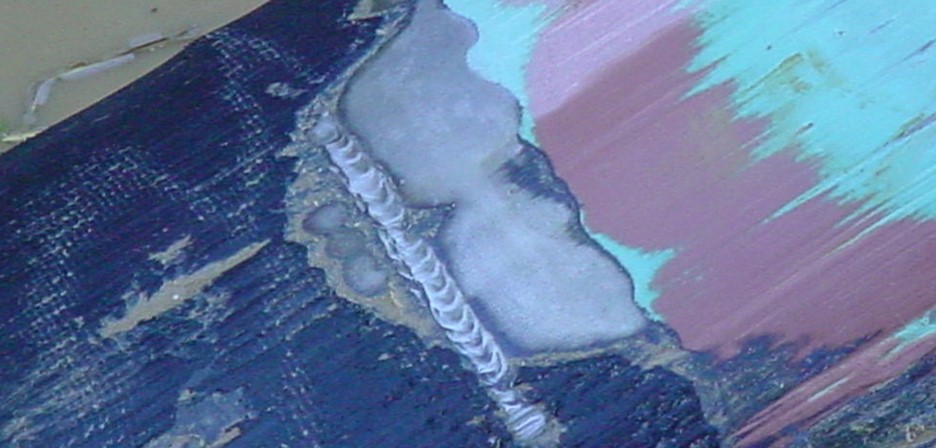
Additionally, geotechnical surveys may fail to provide complete insight of all soil and rock types present. Although the field joint is the most susceptible site of coating failure due to geometric changes in the girth weld, and field applied versus factory applied coatings, the industry is recognizing an increase in damage to factory applied abrasion resistant overcoats (ARO). The climate, surface preparation, and level of quality control are additional challenges not encountered in a plant application. The development of ARO has risen to address these new issues. Adhesion, abrasion resistance, impact and gouging resistance are a few of the key characteristics to possess in suitable coating protection.
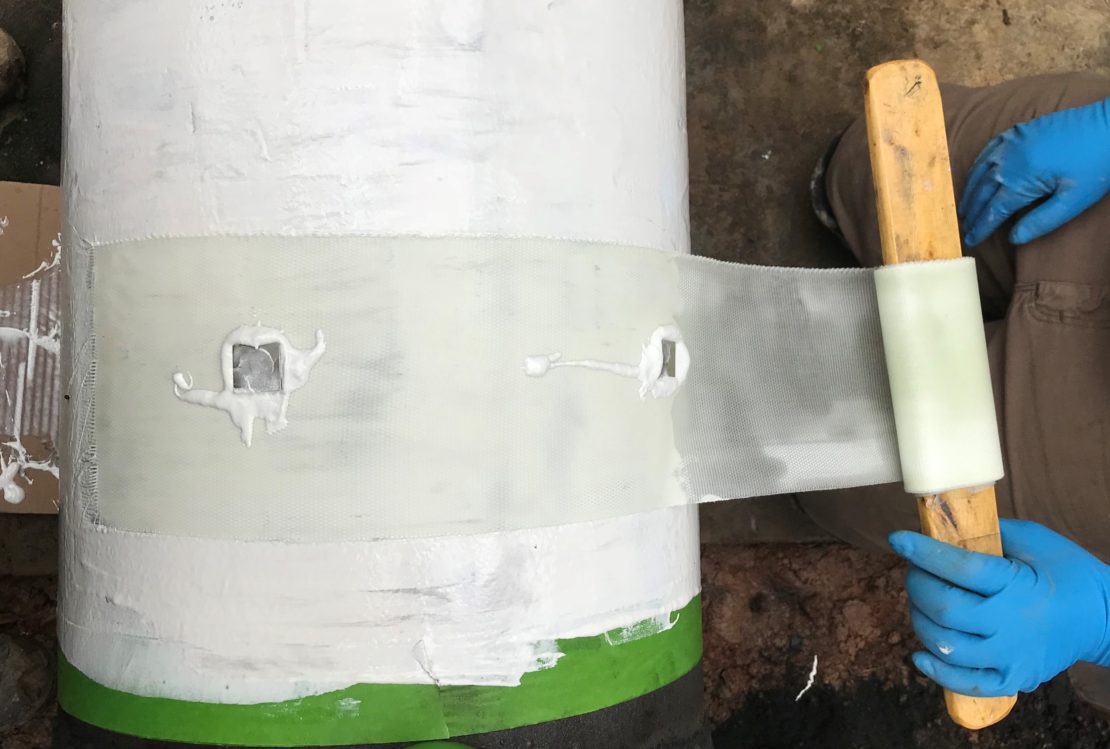
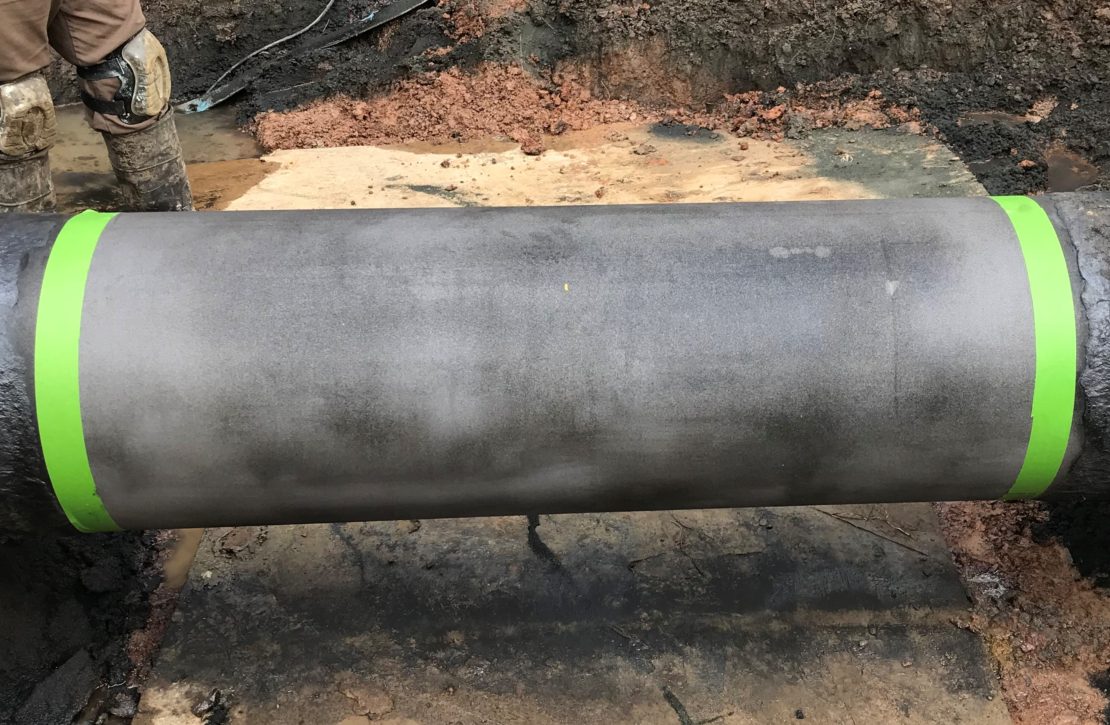
CSNRI’s ScarGuard systems protect and strengthen coatings with proper adhesion, abrasion protection, impact performance and gouging resistance. As a fiber-reinforced polymer, a high fiber-to-polymer ratio provides ideal mechanical properties required for a multitude of damage mechanisms. This moldable wrap forms onto existing anti-corrosion coating, cures rapidly, and builds strength quickly. CSNRI’s ScarGuard product line is there to protect and promote successful HDD installations for your pipeline installation.
Composites are the perfect solution for ARO and coating protection
ScarGuard has been tested and proven against some of the most common and aggressive, defect-causing issues in HDD installations.
- Abrasion – general abrasion and wear can affect the integrity of the mainline or field-joint coatings, causing potential corrosion cells, or at the very least, requiring a heavy amount of cathodic protection.
- Impact – impacts, particularly, as they may occur from tumbling debris or other media in the borehole can cause cracks or other possible issues that can lead to future corrosion cells. Tall girth wells are more susceptible to seeing potential impacts during installation.
- Gouge – gouging can occur during an HDD installation should a rock, or other substance, become stuck in the borehole and begin to cut grooves in or through the existing coatings.
Through the extensive testing and comparisons to real-world performance, it became clear that the above three tests on their own were not telling the full story. Although some epoxy coatings could stand up well to one or more of those tests individually, they still were falling short in real HDD installations. CSNRI went to work to find the differentiator, to ensure continued success of the ScarGuard line of products.
- Fracture Toughness – this property was identified as a key driver in being able to compare laboratory testing to real world performance. Testing for this property has shown that:
- Composites are 10-30x stronger than liquid epoxies.
- Composites are 10-20x stiffer than liquid epoxies.
- Composites generally have 10x great fracture toughness properties than liquid epoxies.
- Full-scale testing
- More recently, CSNRI has worked with world-renowned testing agencies to conduct full-scale testing in laboratory settings to show all of these properties from lab to field and how they can be validated without using actual work sites.
- With the custom test rig created, users can test any type of geological formations in the lab to help guide their decision making in advance of their project.
The Economics of ScarGuard
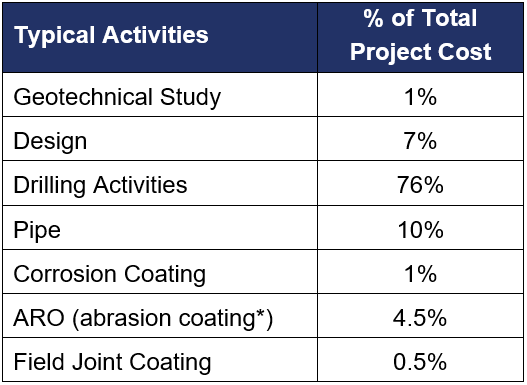
To show the value ScarGuard provides, a cost benefit analysis was conducted to compare the cost of a typical HDD project.
The costs in the table to the right indicate that some of the most important requirements are relatively small compared to the overall project. Coating selection, geotechnical, and design rank the lowest. While the use of ScarGuard may slightly increase the upfront cost of the project, when compared an unsuccessful pullback that must be repeated due to coating failure, it quickly adds extreme value.
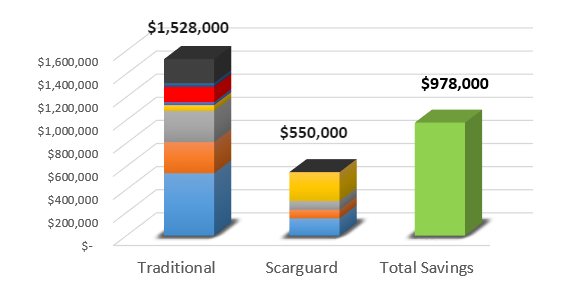
Case Study
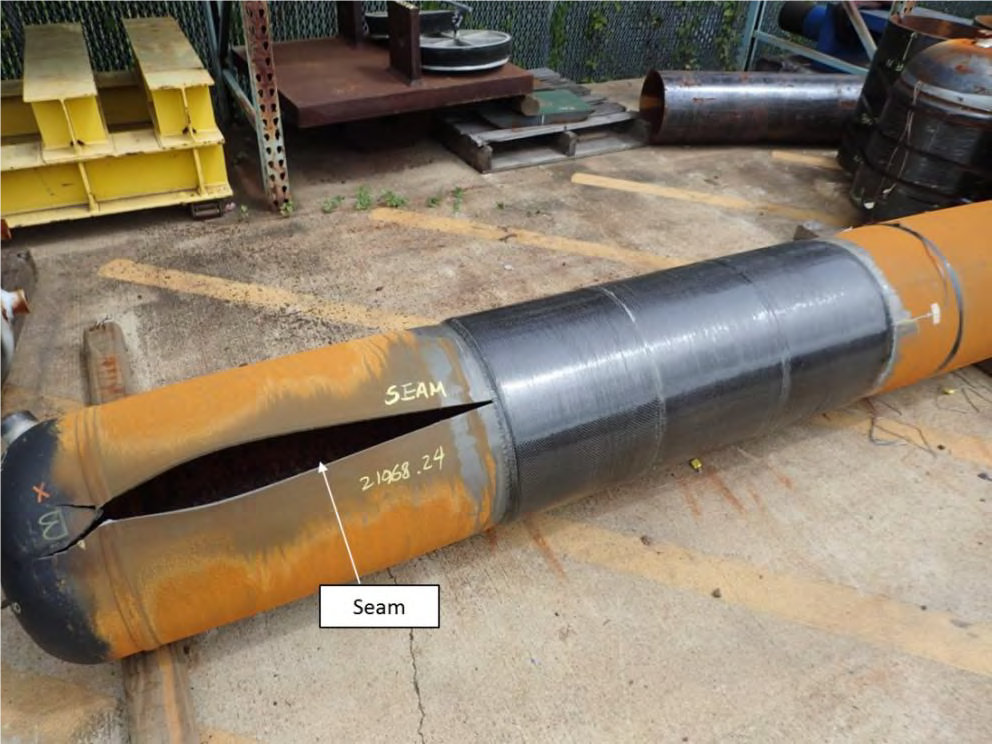
Repulling 3800’/1158m of 20” OD Pipe after damage to FBE caused by HDD.
- After HDD of traditional ARO coated pipe, contractor observed significant damage to FBE coating including gouges along the length and removal of coating over the weld peaks
- Repair costs included additional manpower, equipment, materials, redrill, restring, delay charges, etc.
- Cost difference between repair/repulling versus initial ScarGuard application, almost $1M
More Learning Opportunities
In addition to offering the best products and technical expertise, CSNRI also provides numerous opportunities and methods for increasing your knowledge about composite materials. Composites have been around for centuries, and we’re simply using them in a more advanced way through qualification testing and controlled design scenarios. Whether through in-person meetings, industry publications, or online learning events, we’re here to make sure your questions are answered. We are constantly pushing composite systems to the next level, and we look forward to you joining us on this journey. If you would like to learn more, please visit our TEC talks On-Demand page to see our library of webinars, or contact us today to set up your technical meeting or learning event.


Composites for HDD Coating Protection
Delivered on June 9 & 11, 2020

We pull you through: Ensuring coating protection for HDD applications
Delivered on Nov. 10 & 12, 2020
USAPipe DetailsNew, 24-inch (609.6-mm) steel pipeline was being installed using HDDThe line was being pulled 1,600-ft (488-m) through graniteARO was used to protect the FBE coatingSummaryA gas utility company installed a new, 24-inch (609.6-mm) steel pipeline using HDDThe line was being pulled 1,600-ft (488-m) through graniteScarGuard® was used to protect the FBE coating during installationSmooth…
New YorkPipe DetailsNew, 24-inch (609.6-mm) regulated pipeline was being installed using HDDThe line was being pulled 1,200 feet (366 m) through cobbleThe original ARO failed to protect the pipeline from damageSummaryA company installed a new, 24-inch (609.6-mm) pipeline using HDDThe line was being pulled 1,200 feet (366 m) through cobbleThe original protection failed to protect…









